Understanding Data Handling and Decision-Making: A Case of XYZ Transport Company

Understanding Data Handling and Decision-Making: A Case of XYZ Transport Company
Favour E Markson and E. E. Markson
Abstract
A variety of organisations in this cotemporary time, incorporate data analytics techniques as part of the organisations core values, as this will help businesses better, as well as make informed strategic decisions. This report performs gap analysis in the data infrastructure in XYZ Transport company, the report will discuss data sources in XYZ Transport and the integrity of the data. Performing data gap analysis is of great importance to XYZ Transport company as it enables the company to improve its efficiency, understand its operations better and also ascertain where the company is doing well and what needs to be improved. The report discovers issues with XYZ Transport data sources and how to strategically overcome it which include the adoption of data analytics framework (CRISP-DM), to improve big data infrastructure and as well as address the issues of irregularities in data collected within XYZ Transport company and proffer recommendation such as; integrating platforms for data analytics to accommodate new technologies and implement employee training on data analytics.
Introduction
Perform Data Gap Analysis for an Organisation or Project of your Choice
Brief Background of the Organisation
XYZ is a well-established transport organisation that operates in England. Though there are other transportation organisation who make impact in transportation business, XYZ has been the oldest and key transportation in the country. Its operation cuts across: Road transport and Shipping. XYZ transport provides network transport support that helps businesses as well as assist individuals and goods to travel to their respective destination. The organisation is faced with the challenges of reducing accidents on the road among drivers, dealing with serious driving offences and ensuring road safety. More so, this report is set to identify key sources of data as well as gaps that exist in analytics of data within XYZ Transport; proffer recommendation for decision making.
Identification of Key Data Sources and Datasets available to the Organisation
According to research, data sources are the locations from which a given data is derived from, however, most refined data could also serve as data sources (Talend, 2020). On the other hand, datasets can be viewed as a group of data presented in either a structured or unstructured format (Dataquest, 2020). This report has identified data sources associated with XYZ Transport company as shown in the table below.
Table 1. Key Financial and Non-financial types of data.
No | Data Source | Data Description | Financial or non-Financial | Business Units or Departments Using this Data |
1 | Shipment of goods and order records | Figures from shipments and orders | Non-financial | Operations unit |
2 | Hospital and Police records | Figures of road accidents collected | Non-financial | Operations Unit |
3 | Traffic sensors and traffic cameras | Figures collected from traffic records | Non-financial | Logistics Unit |
4 | Oyster Card and Global positioning System (GPS) | Journey data | Non-financial | Transport unit |
5 | Giving’s to charity | Figures of annual giving for community development | Financial | Finance Unit |
Inspection of Data Integrity and Current or Potential Gaps in Data Analytics and Data Protection.
Research shows that business functions and data sources in XYZ Transport are related as most business functions are seated on heaps of data, thus, utilising the data will enable business functions to reach and make strategic decisions which will enable business functions to achieve (Fletcher 2018) transformed goals. Figure 1 below shows the mapping that exist between data sources and business functions in XYZ Transport.
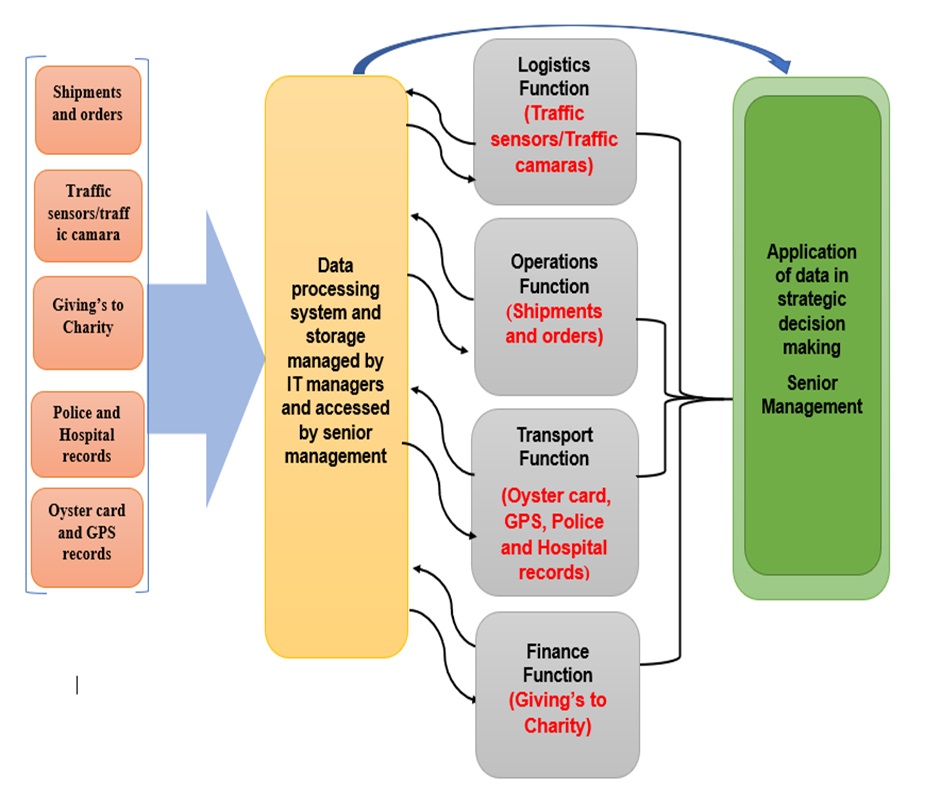
Figure 1. Mapping between business functions and data sources in XYZ Transport Company
The concept of data integrity according to research points out that data integrity deals and describes data validity, quality and ensures that data is correct, complete without corruption (Nikam et al., 2020). Supporting this assertion, literature reveals that data integrity implies generally to the reliability, (Naeem 2020) completeness and accuracy of data. Though, data integrity guarantees safety and confidentiality of (Talend 2020) customers, however, there are drawbacks, that data integrity is subject to compromise either from humans or transfer (Brooks 2020) errors from a system to another. This report has identified gaps that exist in XYZ transport company.
Table 2. Identified Gaps in Data Management
Business Unit or Department | Issues | Data Sources Involved | References to Literature |
Operations unit |
| Shipment records and order of goods record | Cruz (2019) |
Operations Unit |
| Road accident data from Police records and Hospital records. | Deloitte (2017), Naeem (2020) |
Transport Unit |
| Data from Oyster cards and Global Positioning Systems | Zimmer (2018) |
Logistics Unit |
| Traffic sensors and traffic data. | McDowall (2020), TAG (2020) |
Recommendation of Improvements to the Organisational Data Analytics Processes
Based on the findings, the following are recommendations to XYZ Transport company data analytics processes.
- Implement programs on data governance
- Implement data analytics trainings to employee.
- Establish integrated data analytics platforms to accommodate new technologies.
Reorganisation of the Current Data-driven Processes to Streamline and Enhance the Data Analytics and Decision Making.
According to research, Data Analytics is basically an asset (Guarda 2019) for organisations in obtaining competitive advantage, promotes efficiency in operation as organisations can make out potential drawbacks and take necessary action. However, data analytics has been criticised to be subject to data breach (Ciklum 2017). Though data analytics has its limitation, this report will adopt data analytics framework to close gaps identified in XYZ Transport, as the framework will help the data collected to be cleaned to remove inconsistencies in the data, analysed to make informed operational decisions and enhance performance (Biswal 2020).
Below is Table 3, showing proposed data analytics.
No | Data Source | Specific Organisational Decisions | Decision Type (Strategic, tactical, operational) |
1 | Transport management system |
| Tactical |
2 | Employee performance appraisal |
| Strategic |
3 | Freight bills and invoice |
| Operational |
4 | Assets |
| Strategic |
Roadmap to the Development or Enhancement of the Big Data Infrastructure
This report shall adopt CRISP-DM model as the data analytical framework for XYZ Transport company to help build and enhance big data infrastructure and also address the issues of inconsistencies in data collected within the company. Comparing CRISP-DM to SEMMA, another data mining tool, SEMMA according to Saltz and Hotz (2020) skips the business understanding phase and does not address the deployment phase like CRISP-DM. Literature shows that CRISP-DM, offers standardised framework (Chatterjee 2020) for managing and planning a project; allows project replication and encourages best practices. However, Taylor (2017) criticised the use of CRISP-DM that it lacks clarity and does not execute management of project activities. In spite of these drawbacks, research points out that CRISP-DM helps organisations to plan and implement data (Manasson 2019) mining projects so as to deliver real time business (Chatterjee 2020) value. The data analytics implementation process is stated in the table below using CRISP-DM model. See Appendix 1 for CRIP-DM model
Table4. Data Analytics Implementation process
No | Phase of The Big Data Analytics Process | Activities to Be Implemented in XYZ Transport company |
1 | Understanding the business challenge |
|
2 | Understand the data |
|
3 | Preparation of Data |
|
4 | Modelling |
|
5 | Evaluation |
|
6 | Deployment |
|
Compliance Aspect of the Proposed Changes in Data Analytics
There are growing concerns over the issue of confidentiality and protection of personal data, given the increase on how companies obtain, store and utilise data. However, to address these concerns, regulatory frameworks such as the EU GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), have been imposed on organisations that keep or process data of employees to ensure that they are compliant to the data protection laws and maintain good (Small 2019) data governance, and have data security control. Furthermore, the data protection policy as well as ethical assurance (Fabiano 2019) ensures data integrity by granting access to data only to authorised employees and also ensure there is confidentiality of data by making available to employees’ data protection, procedures as well as standards. However, for XYZ Transport company to be compliant, must ensure data protection regulatory standards are adhered to in data analytics processes and ensure that cyber security is well built in to the company system to avoid penetration by external hackers (Starlings 2019). Below is a table on compliance and data protection.
Table 5. Data Protection and Ethical Compliance
| Data Protection/Ethics Requirement | Procedures to be Implemented in the XYZ Transport Company | Relevant Data Protection Standard | References |
1 | Employee data protection |
| GDPR | Fabiano (2019) |
2 | Client data protection |
| GDPR | Small (2019) |
3 | Cyber Security Standard |
| GDPR | Starlings (2019); Moura and Serrao (2020) |
Explain how the proposed big data analytics can be used in the organisational decision making
Research shows that big data stands to be of great use in XYZ Transport company as it has become the important force in transportation and logistics. The adoption of big data will enable XYZ Transport to make realistic data based informed decision on how to make adjustments on daily operations, use big data to deliver real-time (Jessop 2020) insights on the needs of the organisation.
Table 6. Supported Business Decisions
Business Decision | Decision Type
|
To improving measures on how reduce road accidents on major and local roads and also ascertain the cause of these accidents.
| Strategic
|
Implement data privacy and protection as well as enhance cyber security | Tactical
|
To optimise profit and reduce operational cost in transportation within a short period of time | Operational
|
From the above set of business decisions, XYZ Transport shall focus on establishing measures that will reduce road accidents and also ascertain the cause of road crash as this will help to ensure the safety of the individuals and vehicle operators. To achieve this, XYZ Transport shall adopt the use of big data analytics to enable better informed decision making.
Table 7. Business Decision Selected for Analysis
Business Decision | Related Business Question | Decision Type (Strategic, Tactical, Operational) |
To Reduce road accidents |
| Strategic decision |
Biswal, M., 2020. Why Big Data is Important. [Online] Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339229072_Why_Big_Data_Analytics_Important. Accessed on 29 November 2020.
Brook C., 2020. What is Data Integrity? [Online] Available at: https://digitalguardian.com/blog/what-data-integrity-data-protection-101. Accessed on 27 November.
Chatterjee, T, K., 2020.Why using CRISP-DM will make you a better Data Scientist? [Online]. Available at: https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/why-using-crisp-dm-will-make-you-a-better-data-scientist/. Accessed on 1 December 2020.
Ciklum, 2017. Limitations of Big Data Analytics. [Online]. Available at: https://www.ciklum.com/blog/limitations-of-big-data-analytics/. Accessed on 29 November, 2020.
Cruz, A., 2019. What is Transport Management System? [Online]. Available at: https://blog.shiphawk.com/what-is-a-transportation-management-system. Accessed on 30 November, 2020.
Dataquest, 2020. How are Datasets Created. [Online]. Available at: https://www.dataquest.io/blog/free-datasets-for-projects/. Accessed on 26 November 2020
Deliotte, 2017. Under the spotlight Data Integrity in life sciences. [Online]. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/uk/Documents/life-sciences-health-care/deloitte-uk-data-integrity-report.pdf. Accessed on 29 November 2020.
FABIANO, N. and Fabiano, S.L., 2019. Ethics and the Protection of Personal Data. [Online] Available at: http://www.iiisci.org/Journal/CV$/sci/pdfs/ZA486XO19.pdf . Accessed on 27 November 2020.
Fletcher, D., 2018. The Success of Your Business Depends on the Relationship Between IT and Finance. [Online]. Available at: https://qz.com/1413303/the-success-of-your-business-depends-on-the-relationship-between-it-and-finance/. Accessed on 30 November, 2020
Guarda, D., 2019. The Importance of Data Analytics to the Modern World. [Online]. Available at: https://www.intelligenthq.com/importance-data-analytics-modern-world/. Accessed on 29 November 2020.
Jessop, K., 2020. What Is the Impact of Big Data in the Transportation & Supply Chain Industries? 11 Possibilities with Big Data. [Online]. Available at: https://cerasis.com/big-data-in-the-transportation/. Accessed on 1 December 2020.
Manasson, A., 2019. Why Using CRISP-DM will Make You a Better Data Scientist. [Online]. Available at:https://towardsdatascience.com/why-using-crisp-dm-will-make-you-a-better-data-scientist-66efe5b72686. Accessed on 9 December 2020.
McDowall, 2020. Understand the scope of a data integrity program and learn how to perform data process mapping on a chromatographic process. [Online]. Available at: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/articlereprints/public/executivesummary-addressing-data-integrity-gaps-LCGC-openlab-agilent.pdf. Accessed on 29 November 2020.
Moura, J, & Serrao, C., 2020.Security and Privacy Issue of Big Data. [Online]. Available at: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1601/1601.06206.pdf. Accessed on 1 December 2020.
Naeem T, 2020. What is Data Integrity in Database. Why do you need it? [Online]. Available at: https://www.astera.com/type/blog/data-integrity-in-a-database/. Accessed on 27 November, 2020.
Nikam et al., 2020. Data Integrity: An Overview. [Online]. Available at: http://recentscientific.com/sites/default/files/16185-A-2020_0.pdf. Accessed on 27 November 2020.
Small, M., 2019. Big Data Analytics – Security and Compliance Challenges. [Online]. Available at: https://www.comforte.com/fileadmin/Collateral/WP_KC_Security_and_Compliance_Challenges_in_2019.pdf. Accessed on 1 December 2020.
Stalling, W., 2019. Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice. Sixth Edition London: Pearson Education
Talend, 2020. What is a Data Source? [Online]. Available at: https://www.talend.com/resources/data-source/. Accessed on 26 Nov. 2020.
TAG, 2020. Data Sources and Surveys. [Online]. Available at: http://www.gov.uk/transport-analysis-guidance-webtag.Accessed on 20 November, 2020.
Vorhies, W., 2016. CRISP-DM – a Standard Methodology to Ensure a Good Outcome. [Online]. Available at: https://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/crisp-dm-a-standard-methodology-to-ensure-a-good-outcome. Accessed on 4 December 2020.
Zimmer, M., 2018. Addressing conceptual gaps in big data research ethics: An application of contextual integrity. Social Media+ Society, [Online] 4(2), 2056305118768300.
